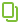
The modern Russian alphabet is derived from the Old Slavonic alphabet. The alphabet originated around 863, and its creators are considered to be the preachers Cyril and Methodius. Many of the letters established by them are still used today in their original form, for example, in the alphabet of the Church Slavonic language. Cyril and Methodius, in Slavic Orthodoxy, are numbered among the saints, and are considered the enlighteners of all Slavs. Today, most digital fonts support Old Slavic characters.
Modern Russian Alphabet:
A B D D E E G H I J J L L N O P S T U F T H C H S H Y Y Y A
An even earlier progenitor of the Russian language is Glagolitic. Glagolitsa is considered to be the first Slavic alphabet, which has little in common with the modern Russian alphabet. However, it was from this alphabet that the Old Slavonic alphabet and then the Russian script originated.
Scientists think that the Cyril and Methodius alphabet has been used since pagan times. However, the mass dissemination of writing began only after the baptism of Russia by Prince Vladimir in 988. At that time educational institutions were established and the process of popularization of the writing among population began. Fonts acquired more regular and proportional lettering.
There were several currents in ancient Russian writing, which were used for different purposes, and by different segments of the population.
Book writing. Statute
The ustavnaya script is one of the forms of ancient Russian writing, which was used for writing state papers and designing books of all directions. The ustavny font had an angular shape, each letter fonts visually fit into a rectangular or square shape. Over time, the semi-uncial appeared with a slant, and the aspect ratios of the characters changed.

Household writing. Shorthand
Shorthand, unlike the charter font, is characterized by rounded, ornate forms. It was used mainly in everyday life and in educational institutions. But not seldom cursive writing was used for state papers (on the photo written decree of Peter I). It differs from other forms of Old Russian scripts by the presence of a large number of ligatures and flourishes which are often connected with each other. It is cursive writing that is the ancestor of the modern handwriting.

Ancient Russian writing has undergone numerous transformations over the years. Below we list the changes that took place in history and greatly influenced the modern Russian alphabet.
Major periods of reform in spelling
- Originally, the Cyrillic alphabet of the Old Slavonic language contained, presumably, 43 letters. Of these, 14, in different periods, were excluded or replaced as being of no use. In this form the alphabet existed until the beginning of the 17th century.
- In 1708-1711, after Peter the Great's reforms, superscripts were removed. At that time, by the way, ceased to exist and the letter "Y", which was returned to the alphabet only in 1735.
- 1917-1918, simplification of Russian writing . Old Church redundant letters, such as "yat" (which was similar in sound to the modern "e"), and "fita" (modern "f") were excluded from the alphabet. Accordingly "Dnepr" became "Dnepr," and "Ѳeodor" became Fedor. The reforms caused a wave of indignation among famous writers and figures of the time.